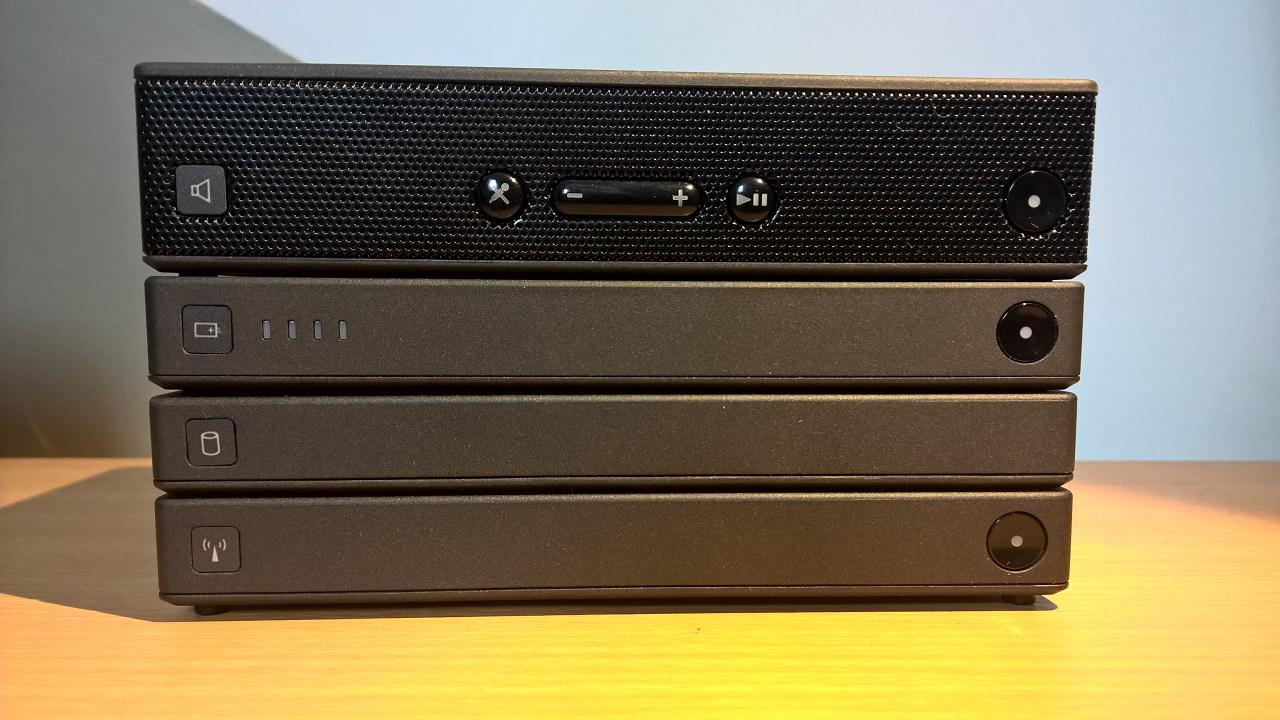
Box Contents
-
ThinkPad Stack Bluetooth Speaker
-
10,000 mAh Power Bank
-
Wireless Router
-
1 TB USB 3.0 Hard Drive
-
Standard USB 3.0 to Micro USB 3.0 Type B Cable
-
Standard USB 2.0 to Micro USB 2.0 Type B Cable
-
Aux-in Cable
-
Pouch
-
Lenovo 10 W AC Adapter
-
Warranty and User Guide
Installation
Access Point
When I unpacked the ThinkPad Stack for the first time, I was quite confused, because I didn’t know where to get started. But the first thing you should do is to visit http://www.lenovo.com/stack and install the software on your computer. This will be very useful to configure the Access Point.
Alternatively, there is also a more advanced method available where you visit the ThinkPad Stack using its IP address and configure it in your browser. This is explained at a later point in this review.
You can also connect the USB charger directly to the access point module.
Battery
To use the battery, you charge it with the included USB adapter/charger and USB2.0 cable and you stack it with the other ThinkPad Stack modules. Note that it can take several hours to fully charge the ThinkPad Stack battery module.
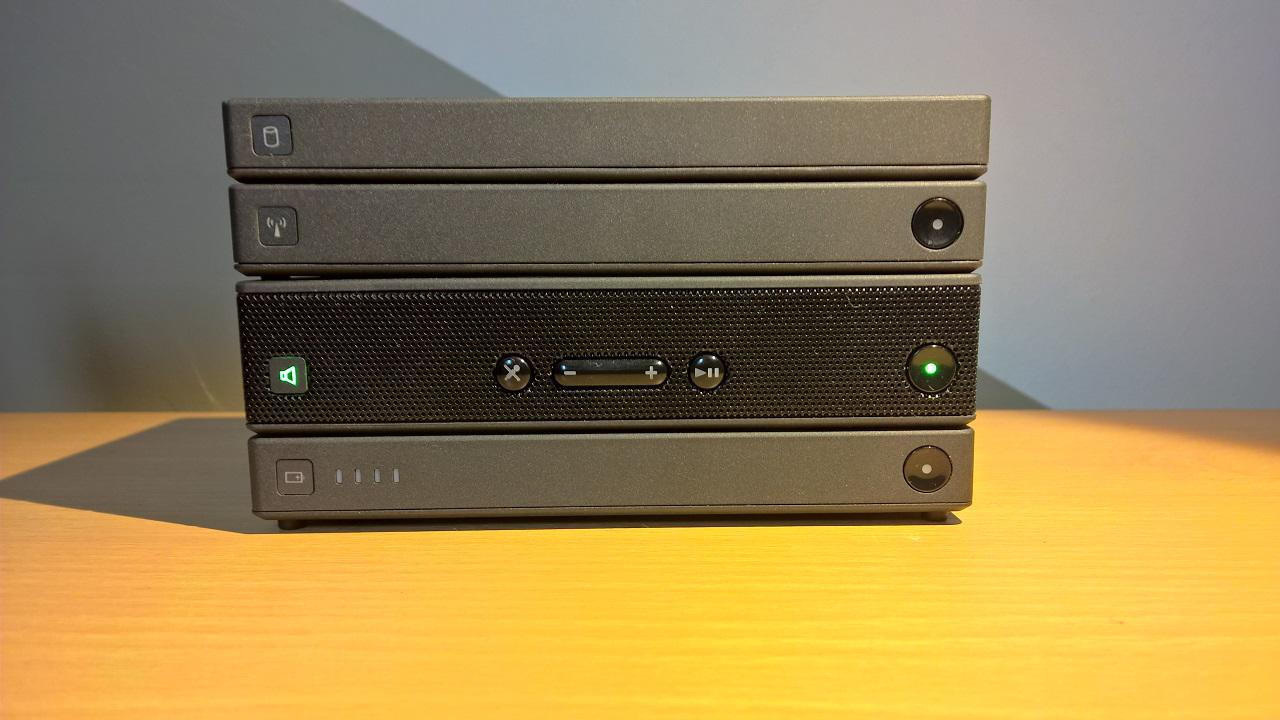
Speakers
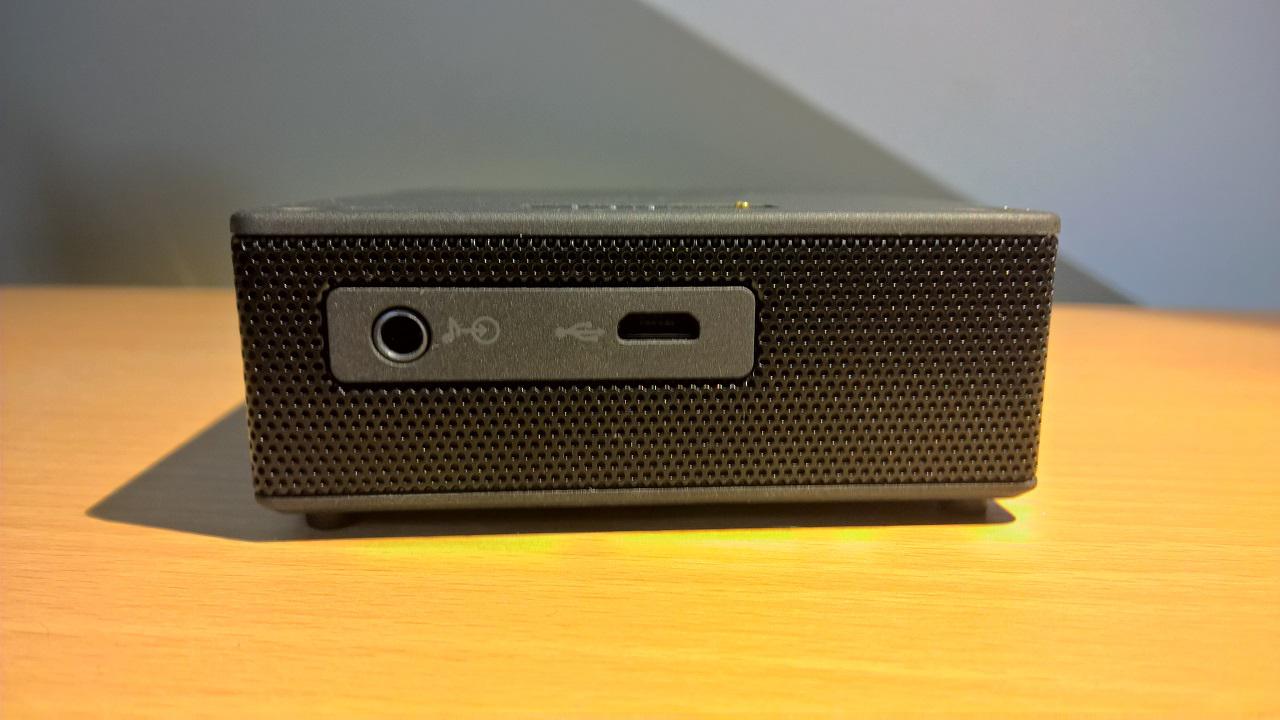
Aux-in (audio in cable)
You can use the included aux-cable to play music using a wired connection. Then you don’t rely on Bluetooth. This is probably the most reliable as Bluetooth connections can always drop. This is a really useful future.
Bluetooth
The speakers will be hard to setup without a manual, because it doesn’t seem really obvious on how to pair the speakers with another Bluetooth device.
Here are the steps that should be taken before you drop the bass:
-
Press the ‘Power’ button on the right of the speaker module. You will hear a beep and see the volume icon on the left being lit up together with the power button on the right.
-
Now long press the power button until you hear two beeps (one low pitch beep followed by a higher pitch beep).
-
Grab your smartphone, tablet, computer and start searching for bluetooth devices.
-
The ThinkPad Stack may show up as ‘headphones’, ‘speakers’ or as ‘ThinkPad Stack’.
-
Now connect to the ThinkPad Stack’s Bluetooth speakers.
Hard drive
Use the included USB3.0 cable and plug it in your computer. You will see a few folders that have been already made for you. Note that if you encrypt it with Bitlocker, it may not show up as a network drive.
Modules
Access Point
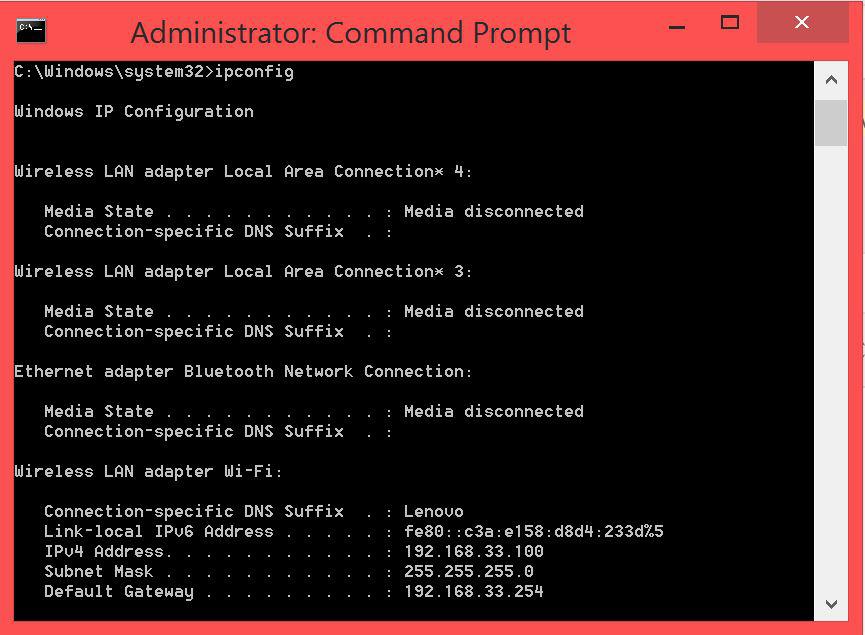
An alternative way is to open command prompt, and then enter:
ipconfig
Then retrieve the ‘default gateway’ IP address and enter it in your browser.
Then just below the QR code, you will see the login form where you enter your username and password.

Operation Mode
-
Gateway (default): In this mode you connect the etnernet cable from your main router to your ThinkPad Stack to use the ThinkPad Stack as access point.In this mode, the device is supposed to connect to internet via ADSL/Cable Modem. The NAT is enabled and all the wireless clients share the same IP through WAN port to ISP. The connection type can be setup in WAN page by using PPPOE, DHCP client, PPTP client, L2TP client or static IP…
-
Bridge: In this mode, all ethernet ports and wireless interface are bridged together and NAT function is disabled. All the WAN related function and firewall are not supported. In bridge mode, the clients will obtain an IP address from the primary router.
-
Wireless ISP: In this mode, all ethernet ports are bridged together and the wireless client will connect to ISP access point. The NAT is enabled and PCs in ethernet ports share the same IP to ISP through wireless LAN. You can connect to the ISP AP in Site-Survey page. The connection type can be setup in WAN page by using PPPOE, DHCP client, PPTP client , L2TP client or static IP.
Wireless
2.4G/5G wireless
Basic Settings
| This setting will enable or disable the 2.4GHz or 5GHz band. |
| On 2.4 GHz band: * 2.4 GHz (B) * 2.4 GHz (G) * 2.4 GHz (N) * 2.4 GHz (B+G) * 2.4 GHz (G+N) * 2.4 GHz (B+G+N) (recommended, fastest on 2.4 GHz) On 5GHz band: * 5GHz (A) * 5GHz (N) * 5GHz (A+N) * 5GHz (AC) * 5GHz (N + AC) * 5 GHz (A + N + AC) (recommended, fastest on 5 GHz) |
| * AP: Connect an ethernet cable to the ThinkPad Stack in order to get internet connectivity. * Client * WDS: Simply put, it enables single-radio APs to be wirelessly connected instead of using a wired Ethernet connection * AP+WDS |
| * Infrastructure * Ad hoc Only available if 'Mode' is set to 'Client'. |
| The name of the wireless network that will be broadcasted in the air. |
| On 2.4 GHz band: * 20MHz * 40MHz (fastest on 2.4 GHz) On 5 GHz band: * 20MHz * 40MHz * 80MHz (fastest on 5 GHz) Increasing the channel width may increase network bandwidth. May possibly decrease performance with increased range in noisy environments. |
| Auto |
| Set the channel the 2.4 GHz or 5GHz radio is using. It is recommended that you leave this setting at 'Auto'. This way, the ThinkPad Stack can choose a channel that is not occupied or being overlapped by another AP. |
| * Enabled: Shows the wireless network. * Disabled: Hides the wireless network, forces you to enter SSID manually to connect to the wireless network for the first time. If you want to hide the existence of your wireless network, then set this to disabled. But may be harder to connect to for someone without the knowledge on how to find the wireless network using SSID... |
| * Enabled * Disabled WMM prioritizes traffic according to four Access Categories (AC) - voice, video, best effort, and background. It is suitable for well defined applications that require QoS, such as Voice over IP (VoIP). |
| With this setting you can control the maximum data rate for the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz band. It is recommended you leave this setting at 'Auto'. |
| 0 Mbps (default, no restrict) With this setting, you can limit upload bandwidth. |
| 0 Mbps (default, no restrict) With this setting, you can limit download bandwidth. |
| Possibly shows all connected clients to the 2.4 GHz or 5 GHz radio. |
| Using this mode, the ThinkPad Stack connects to the existing wireless network, but just repeats the radio signals. Enable this to extend the range of the existing wireless network. Repeater Mode may be prone to decreased performance in noisy environments, possibly duplicating corrupt network packages. |
| ? |
Advanced Settings
| 2346 (256 - 2346) If your wireless network is experiencing a lot of collisions, try adjusting 'Fragmentat Threshold' to improve throughput. |
| 2347 (0 - 2347) When medium is too noisy or lot of interference is present. The AP/Station if it is not getting chance to send the packet it can initiate RTS/CTS mechanism to get a chance to send the packet to avoid collision. |
| 100 ms (20 - 1024) This represents the amount of time between beacon transmissions. Before a station enters power save mode, the station needs the beacon interval to know when to wake up to receive the beacon (and learn whether there are buffered frames at the access point). The higher the value, the greater the lag or delay, because the beacon is sent less frequently. Lower value may decrease lag, decrease throughput and increase power consumption. |
| Enabled (Enabled / Disabled) IAPP = Inter-Access Point Protocol (802.11f) |
| Disabled (Enabled / Disabled) |
| Enabled (Enabled / Disabled) |
| Enabled (Enabled / Disabled) Short GI = Short Guard Interval Only works with 802.11n and/or 802.11ac enabled. Lowering 'Short GI' can increase throughput. In bad multipath situations, use a higher value to increase reliability. |
| Disabled (Enabled / Disabled) Prevents WLAN clients and LAN clients from communicating with eachother. |
| Enabled (Enabled / Disabled) STBC = SpareTime Block Code Can extend wireless range by using an extra antenna per transmission. |
| Enabled (Enabled / Disabled) |
| Disabled (Enabled / Disabled) If disabled, it will force 40 MHz as 'Channel Width' for the 2.4 GHz band. If enabled, it will prefer 20 MHz as 'Channel Width', but may still allow clients using 40 MHz 'Channel Width'. Requires: * 2.4 GHz band only |
| Enabled (Enabled / Disabled) Allows the antenna's to boost their wireless range in one direction, so throughput is improved to send/upload data. May possibly cause disconnects for clients located at the opposite side of the access point. |
| Enabled (Enabled / Disabled) When live video is being broadcasted over a LAN or WLAN network, it is possible to use two transmission methods: multicast streaming or unicast streaming. Mutilcast: * Less bandwidth * Lower video quality * No additional overhead with extra clients Unicast: * Guarantee minimum level of QoS for vieo quality via one-to-one session estabilishment * More bandwidth * Overhead with extra clients Enabling this setting will guarantee maximum video quality to a large number of clients |
| * 100% (default): maximum power consumption & maximum range * 70% * 50% * 35% * 15% Specify how much power is used to power the antenna's. Higher values increase power consumption and have a higher wireless range. |
Security
| Select the SSID you want to modify security settings for. |
| * Disabled: unsecure/public, no encryption, fast * WEP: compatible with older WLAN chips, easy to crack * WPA2 (default): safest, fast * WPA mixed: slower Choose WPA2 by preference, because it is the most secure and more or less the best you can choose. Use WEP or WPA-Mixed in case of compatibility issues. |
| * Enterprise (RADIUS) * Personal (Pre-Shared Key) Requires: * Encryption: WPA2 / WPA-Mixed |
| * TKIP The type of encryption used. Requires: * Encyption: WPA-Mixed |
| * AES The type of encryption used. Requires: * Encryption: WPA2 |
| * Passphrase * Hex (64 characters) Requires: * Encryption: WPA2 / WPA-Mixed |
| Requires: * Encryption: WPA2 / WPA-Mixed |
| Requires: * Encryption: Disable/WEP |
| * Open System * Shared Key * Auto Requires: * Encryption: WEP |
| * 64-bit * 128-bit Longer key length means greater security. Requires: * Encryption: WEP |
| * ASCII (5 characters in 64-bit / 13 characters in 128-bit) * Hex (10 characters in 64-bit / 26 characters in 128-bit) Requires: * Encryption: WEP |
| The password for your wireless network. Requires: * Encryption: WEP |
Access Control
Wireless Access Control Mode:
-
Disabled: Disables MAC filtering
-
Allow listed: Only the clients whose MAC address is listed, are able to connect to the wireless network. (Whitelist)
-
Deny listed: Disallow access to clients whose MAC address is listed. They will not be able to connect. (Blacklist)
For your own good, I would not recommend using whitelist-mode (Allow listed). It is a pain to keep up, and will cause you nothing but problems if you purchase a new wireless device or want a friend to connect.
Because of this, I only recommend using MAC filtering to blacklist people who try to abuse your wireless network. Note that using MAC filtering to blacklist someone is not 100% safe, as they only have to buy a new wireless adapter to get past this security. Or they can simply try to spoof/fake a different MAC address.
WDS settings
Wireless Distribution System uses wireless media to communicate with other APs, like the Ethernet does. To do this, you must set these APs in the same channel and set MAC address of other APs which you want to communicate with in the table and then enable the WDS.
Site Survey
?
WPS
This page allows you to change the setting for WPS (Wi-Fi Protected Setup). Using this feature could let your wireless client automically synchronize its setting and connect to the router in a minute without any hassle using a PIN-code instead of using a long password.
Note that leaving Wi-Fi Protected Setup enabled is also less secure.
Schedule
You will be able to enable or disable the 5GHz wireless radio depending on the schedule you define. You will likely use this for power saving purposes at night.
2.4G wireless
TCP/IP Settings
LAN Interface
| Specify the IP address of the ThinkPad Stack |
| * Disabled: Clients will have to use static IP addresses. * Client * Server: In this mode, the ThinkPad Stack can distribute IP addresses to its clients. |
| Specify the range of IP addresses that is automatically assigned to clients that connect to the ThinkPad Stack. By preference, you want to have the range of IP addresses distributed by the DHCP server smaller than the range of IP addresses supported by your network. I usually leave some IP addresses to be distributed manually. |
| Every X amount of minutes, the client will be assigned a new IP address by the DHCP server. (Doesn't have to be necessarily the same) |
WLAN Interface
| * Static IP * DHCP Client: Retrieves an IP address from the DHCP server from the network it is connected to. * PPPoE * PPTP * L2TP * USB3G: Use this settings for USB LTE/3G adapters |
| * Continuous * Connect On Demand: Uses less power * Manual |
| Universal Plug and Play (UPnP) is a set of networking protocols that permits networked devices, such as personal computers, printers, Internet gateways, Wi-Fi access points and mobile devices to seamlessly discover each other's presence on the network and establish functional network services for data sharing, communications, and entertainment. UPnP is intended primarily for residential networks without enterprise-class devices. |
| If enabled, you will be able to ping the WAN-port from anywhere? (not sure) |
In this section, you can also enter a custom DNS server in case your ISP or network at work is blacklisting domain names or websites. Does not work if your ISP or network is blacklisting these servers by IP address.
My favorite alternative DNS server is the one from Google:
Primary DNS: 8.8.8.8 Secondary DNS: 8.8.4.4

Firewall
Port Filtering
Port filtering is used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network to Internet through the Gateway. Use of such filters can be helpful in securing or restricting your local network.
IP Filtering
IP Filtering is used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network to Internet through the Gateway. Use of such filters can be helpful in securing or restricting your local network.
MAC Filtering
MAC Filtering is used to restrict certain types of data packets from your local network to Internet through the Gateway. Use of such filters can be helpful in securing or restricting your local network.
Port Forwarding
Port forwarding allows you to automatically redirect common network services to a specific machine behind the NAT firewall. These settings are only necessary if you wish to host some sort of server like a web server or mail server on the private local network behind your Gateway’s NAT firewall.
URL Filtering
URL filter is used to deny LAN users from accessing the internet. Block those URLs which contain keywords.
For your own good, do not use ‘white list mode’ for URL filtering, you cannot possibly white list every website on the internet.
DMZ
A Demilitarized Zone is used to provide Internet services without sacrificing unauthorized access to its local private network. Typically, the DMZ host contains devices accessible to Internet traffic, such as Web (HTTP ) servers, FTP servers, SMTP (e-mail) servers and DNS servers.
VLAN
VLANs are created to provide the segmentation services traditionally provided by routers. VLANs address issues such as scalability, security, and network management.
QoS
Entries in this table improve your online gaming experience by ensuring that your game traffic is prioritized over other network traffic, such as FTP or Web.
| Enables/disables automatic QoS for uploads/uplink |
| Allows you to specify the amount of bandwidth reserved for uploads. |
| Enables/disables automatic QoS for downloads/downlink |
| Allows you to specify the amount of bandwidth reserved for downloads. |
You can set QoS rules on a per device basis by IP address or by MAC address.

Route Setup
Dynamic Route
Enable/Disable dynamic routing.
| * Enabled * Disabled |
| * Disabled * [RIP 1](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Routing_Information_Protocol) * [RIP 2](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Routing_Information_Protocol) |
| * Disabled * [RIP 1](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Routing_Information_Protocol) * [RIP 2](https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Routing_Information_Protocol) |
RIP is classified as an Interior Gateway Protocol (IGP). Nowadays, RIP has been replaced because of its simplicity and its inability to scale to very large and complex networks.
Each RIP router maintains a routing table, which is a list of all the networks it knows how to reach, along with the distance to that destination. RIP uses a distance vector algorithm to decide which path to put a packet on to get to its destination. It stores in its routing table the distance for each network it knows how to reach, along with the address of the “next hop” router – another router that is on one of the same networks – through which a packet has to travel to get to that destination. If it receives an update on a route, and the new path is shorter, it will update its table entry with the length and next-hop address of the shorter path; if the new path is longer, it will wait through a “hold-down” period to see if later updates reflect the higher value as well, and only update the table entry if the new, longer path is stable.
Using RIP, each router sends its entire routing table to its closest neighbors every 30 seconds. (The neighbors are the other routers to which this router is connected directly – that is, the other routers on the same network segments this router is on.) The neighbors in turn will pass the information on to their nearest neighbors, and so on, until all RIP hosts within the network have the same knowledge of routing paths, a state known as convergence.
If a router crashes or a network connection is severed, the network discovers this because that router stops sending updates to its neighbors, or stops sending and receiving updates along the severed connection. If a given route in the routing table isn’t updated across six successive update cycles (that is, for 180 seconds) a RIP router will drop that route, letting the rest of the network know via its own updates about the problem and begin the process of reconverging on a new network topology.
Static Routing
Static routing is useful if you don’t make a lot of changes to your network, but may be prone to downtime if a router fails.

Management
Status
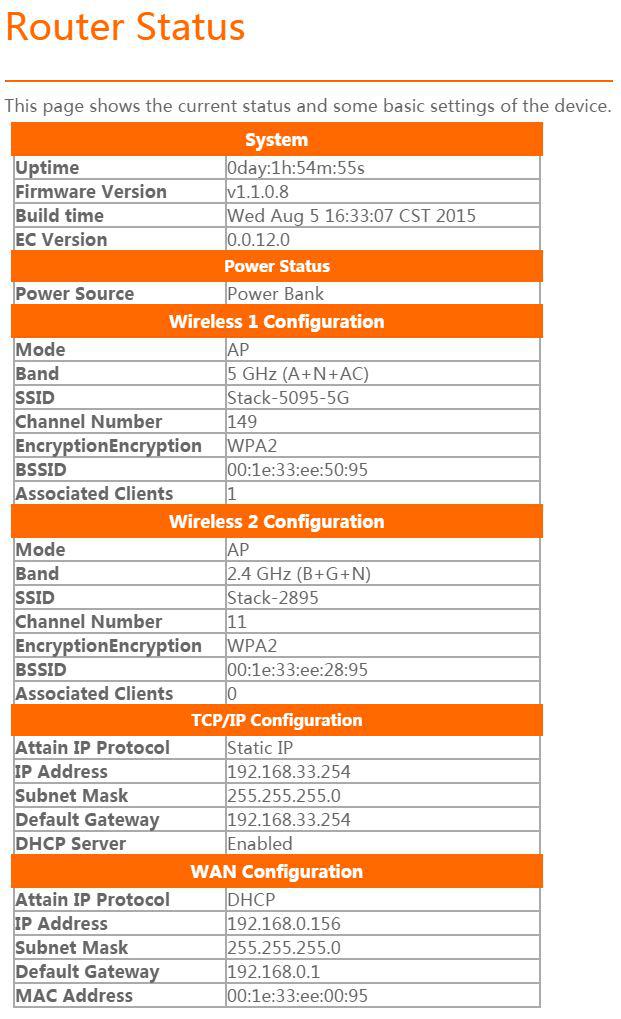
The ‘Status’ screen shows a quick overview of very useful information.
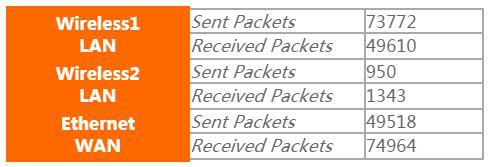
Statistics
View the amount of packets sent or received on a per interface basis. I wish it was a little bit more complete, for example with packet size, to make it easier to read.
DDNS
If you want to access your ThinkPad Stack from a different location for what-ever reason and the IP address of the ThinkPad Stack changes all the time. You can use a domain name to find the ThinkPad Stack rather than using a dynamic IP address.
Note that DDNS may require port forwarding to work properly in some situations.
To use DDNS, you will need a ‘DDNS Service Provider’:
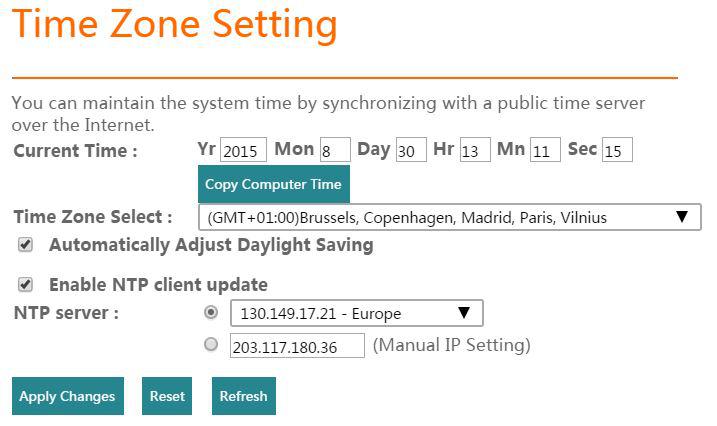
Time Zone Setting
Not exactly sure what it does. Does it synchronize time for all the connected clients? Or do you simply set the time here for readability of the logs generated on the ThinkPad Stack?
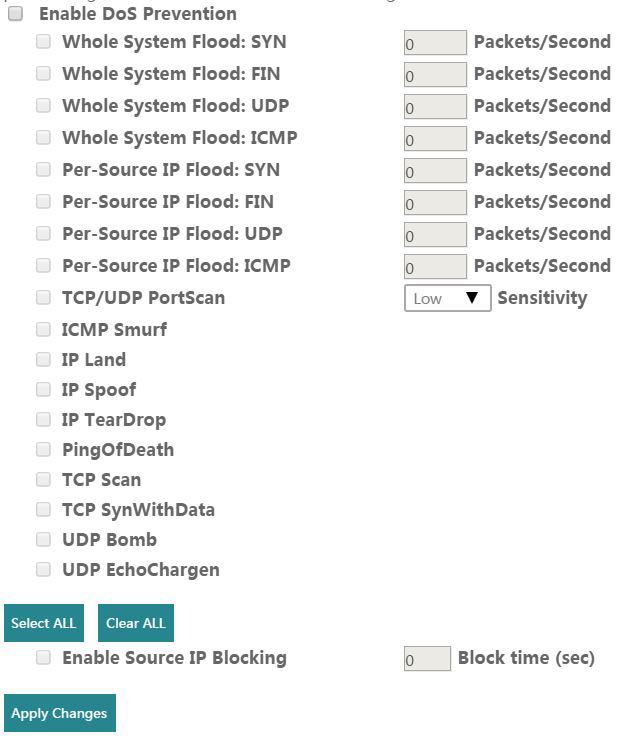
Denial-of-Service
A denial of service (DoS) attack is an incident in which a user or organization is deprived of the services of a resource they would normally expect to have. In a distributed denial-of-service, large numbers of compromised systems (sometimes called a botnet) attack a single target to overload the target until it goes offline.
You are able to configure the sensitivity of the DoS protection on the ThinkPad Stack.
Log
Here you can log system events, DoS attacks and so on. I leave this setting disabled for improved battery life.
Upgrade Firmware
If you download the latest firmware for the ThinkPad Stack, you can upload it manually to the ThinkPad Stack using this screen. I recommend using the ThinkPad Stack App instead.
Save/Reload Settings
Save your settings to a configuration file so you have a back-up of your settings. This is useful if you want to use the same settings on another ThinkPad Stack or if you want to do a reset of the ThinkPad Stack.
Password
Here you can change the password of the ‘admin’ account on the ThinkPad Stack. Make sure to choose a unique password that is not easy to guess.
Hard Drive
The ThinkPad Stack comes with a 1TB hard drive. This is plenty to store all your data. The hard drive model is a Samsung Momentus ST1000LM024. Here are the specifications in a table.
| 1TB |
| SATAIII / SATA 6.0 Gbps |
| 5400 RPM |
| 12 ms |
| 5.6 ms |
| 4 seconds |
| * media to/from buffer: 145 MB/s * buffer to/from host: 300MB/s |
| * Idle: 2.4 Bel3 * Performance seek: 2.6 Bel |
| * Voltage : +5V ± 5% * Spin-up Current (max): 1000 mA * Seek (avg): 2W * Read/Write (avg): 2.3W * For reported capacity: 0.7W * Standby (avg): 0.2W * Sleep (avg): 0.2W |
| Yes |

The battery might also draw power from the battery pack when it is plugged in your computer. Which is something I didn’t really like. I was rather hoping it would rather draw all the power from the USB3.0 hub from my ThinkPad W540.
Note that the hard drive also works without the battery pack attached. The USB3.0 cable is able to provide enough power. Which means that you don’t have to bring the whole ThinkPad Stack if you only need the hard drive.
The hard drive is non-replaceable at first sight. I don’t see any screws, which means you might have to pry it open and risk breaking something.
Tip: disconnect the hard drive from the stack if you do not use it, otherwise it will draw power.
Battery
The battery module has a capacity of 10000 mAh. With the Bluetooth speakers you can expect playback of up to 48 hours. Note that you can also combine multiple battery packs to increase battery life of the ThinkPad Stack.
The battery module has two USB-ports that you can use to charge your smartphone or tablet.
Speakers
Parts
If you ever need to buy parts, this table below may help you:
| Worldwide | 4XV0H34181 | 03X6906 |
| Worldwide | 4XV0H34183 | 03X6907 |
| Worldwide | 4XH0H34184/5/6/7/8/ 4XH0H34339 | 03X6908 |
| US, Canada | 4XH0H34184 | 03X6909 |
| PRC | 4XH0H34185 | 03X6910 |
| Japan | 4XH0H34186 | 03X6911 |
| EU | 4XH0H34187 | 03X6912 |
| UK | 4XH0H34339 | 03X6912 |
| ANZ | 4XH0H34188 | 03X69013 |
Scenario’s
Finding the right use for the ThinkPad Stack might be something you cannot think of right away. But I managed to get very good use out of the ThinkPad Stack by just doing daily life tasks.
As a mobile access point, the ThinkPad Stack might be able to save your day. When I moved to my girl friend’s house, first thing I noticed was that the electricity was very unstable. We would sometimes be without power for 1-2 hours because the electricity circuit of the house is too old. But if you are working at home, this also means you cannot do anything during this time. But what I did was, I purchased a USB 4G LTE dongle from D-Link for 80 EUR to plug in the ThinkPad Stack. Then I got a unlimited data plan for 35 EUR per month which is quite cheap if you need a lot of 4G bandwidth. For a road warrior like me that uses remote desktop connections a lot at work to manage multiple servers, it is a deal breaker. Everything combined I have a very good emergency package for very demanding situations. And if the electricity in the house dies, everyone at home will still have internet access. Isn’t this beautiful? I have to say that everyone at home loves the ThinkPad Stack, just to get us through those tough hours without electricity.
When commuting or travelling to work or to friends, I always want to charge my when travelling by car. But since my car only has one USB-port, an extra USB-port would have been welcome. So now I take the ThinkPad Stack with me in the car and two smartphone charger cables so me and my girl friend and/or my colleagues can charge our phones while travelling by car.
Verdict
The ThinkPad Stack Professional Kit delivers a lot for the amount of money you pay (~260 EUR on www.ok1.de). A decent router costs at least 100 EUR, and a hard drive of 1TB usually goes for 40-50 EUR. So everything else considered. The ThinkPad Stack Professional Kit is a great deal!
The hard drive module is very pleasant to use. I only expected the USB3.0 performance to be a little bit higher. For the second generation ThinkPad Stack I would like the hard drive to be customer replaceable. This way people can replace it with a 2TB hard drive or maybe a solid state drive if desired.
When the HDD module was plugged in my computer and when I was reading/writing files, I also noticed it would still draw power from the battery pack if it was still attached. Be careful with that you don’t end up as surprised as I was. But this is nothing to worry about.
Another small tip, if you use the access point together with the battery pack, you may also want to disconnect the hard drive module if not in use. If the access point is turned on, the hard drive module will also turn on, if attached. This is also a tip in the manual (thank you Lenovo).
The only disappointment in the kit was the speakerset that delivered low quality sound. The speakers from my Nokia Lumia 930 and other ThinkPads deliver better sound quality. The speakers may be best combined with lower-end to mid-end smartphones. The range of the Bluetooth was quite acceptable up to 10-20 meters outdoors. I could still leave my smartphone in my pocket and walk around without the speakers disconnecting.
The access point has so many options available, that I was drooling all over my spill proof keyboard of my ThinkPad W540. The mobile access point or mobile router module is the best part of the whole kit. As you just read in my review, there are plenty of advanced options to explore and tweak to your needs. Whether you are a geek or an IT administrator or a normal person, the ThinkPad Stack is the perfect access point, router or modem you can use to learn. I have never seen so many options in a router in my whole life. Much pleasure guaranteed. Although built-in documentation from Lenovo would have been really helpful. I was unable to document some of the options.
Last but not least the battery module delivers quite good battery life and can be extended with as many battery modules as you like. As far as I have read all documents, at least 2 battery modules is guaranteed to be supported to deliver twice the designed battery life. Or you can charge one battery module and then use the other while you are exploring or using the other one.
If you are the travelling kind of person, do not hesitate to get the ThinkPad Stack, and do get a USB LTE adapter with a good data plan to get the most out of this beautiful device! Then create a mobile access point in your car as you travel! Your passengers will be very happy. Even for professional use I would recommend the ThinkPad Stack, for example in taxi’s.
To finish this review, note that all modules are individually on sale on the Lenovo website! You may want to put together your own package depending on your lifestyle!